What is a citizen developer?
Role of citizen developer in a low-code software development process
A citizen developer is an individual capable of constructing applications without coding expertise, typically with assistance from IT professionals. These practitioners often emerge from various professional backgrounds, ranging from sales executives seeking better administrative tools to payroll administrators aiming to automate processes and boost efficiency.
Regardless of their origin, citizen developers share a common trait: a deep understanding of specific organizational business processes or tasks. This expertise helps them to identify opportunities for operational enhancement and customer service improvement, driving innovation and digital transformation initiatives forward. Whether they are internal employees or external consultants, citizen developers show a readiness to initiate change and create solutions that align with the requirements of their teams, departments, or customers.
Meet Jessie, she’s a citizen developer and configurator working with Betty Blocks. Being a company accountant, she also has a basic technical knowledge and dedication to optimizing business processes within her team.
Jessie’s time on the platform is limited to up to 4 hours per week, and her main tasks include making small changes here and there: adjusting forms, and configurations, and customizing visual elements of the user interface via the theme builder. Sometimes Jessie can work with templates and create a simple overview page.
However, every time she gets stuck with something, Jessie can address her questions to James, a business technologist with a solid understanding of programming and application development.
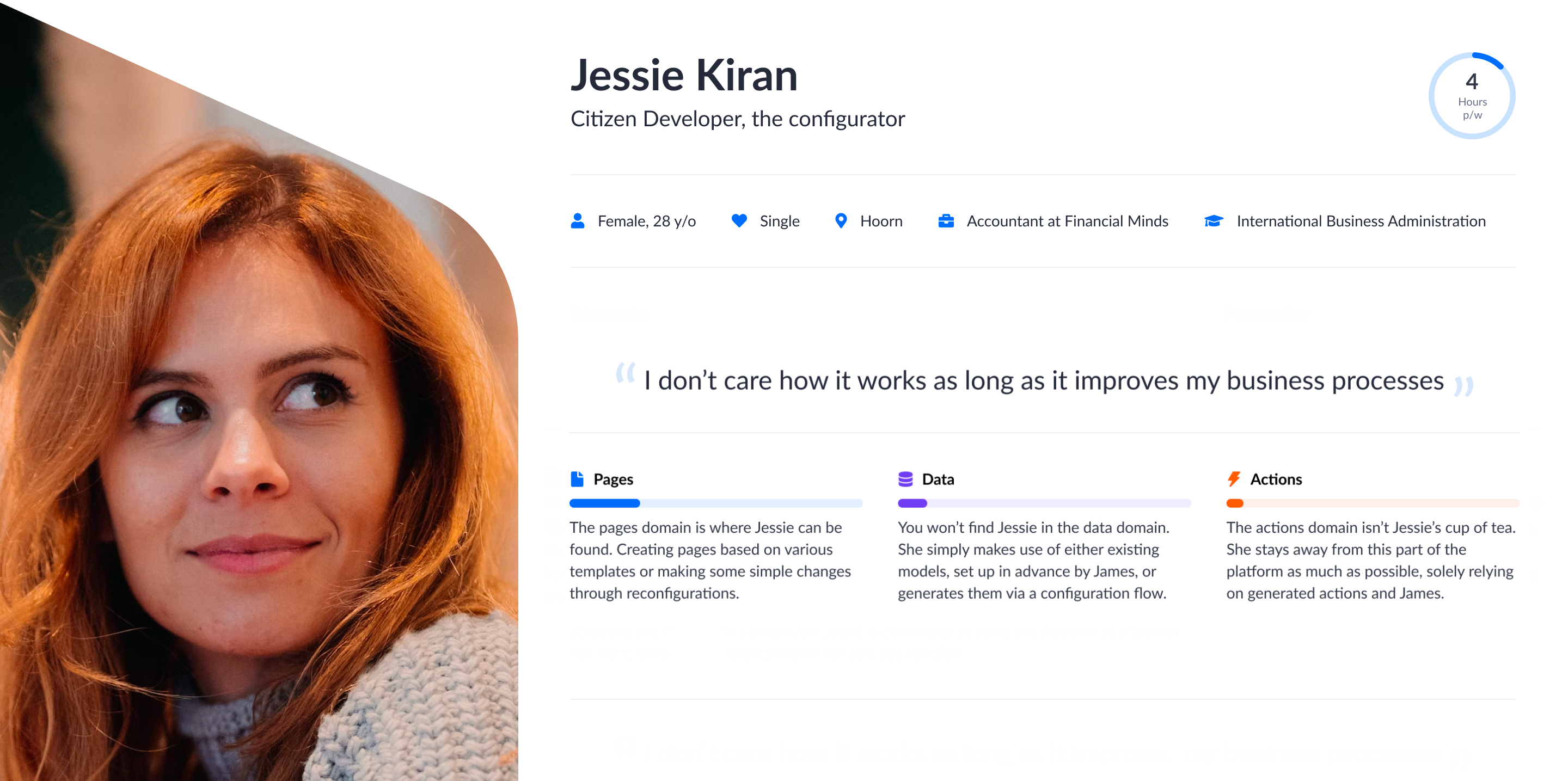
A user portrait like this can already give you a hint about the focus and responsibilities of an average citizen developer. In a more general sense, they are the following:
-
Configuration and maintenance: managing existing applications, tweaking settings, and adjusting functionalities to meet evolving business requirements.
-
Small updates: citizen developers are skilled at navigating through the platforms' interface to give minor changes and improvements to the current workflows based on user feedback or changing business needs. This can include fixing a bug, adding a new field to a form, or changing emails.
-
Front-end changes: modifying the visual elements and user interface of applications. From redesigning layouts to customizing color schemes, they can enhance the user experience without diving into coding languages.
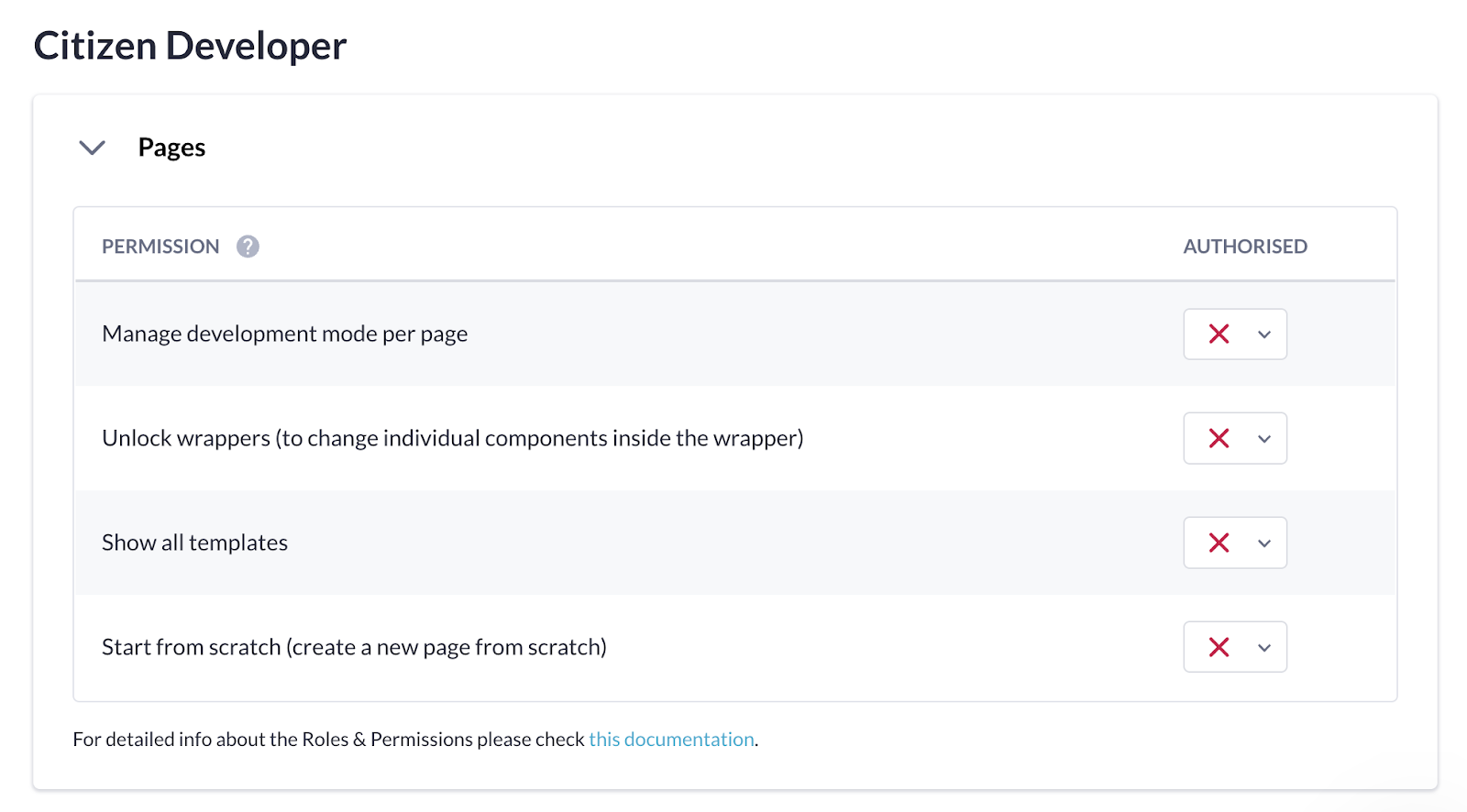
The permissions for citizen developers are turned off by default, though the application/organization admin can provide access to resources such as pre-built page templates, reusable blocks, and drag-and-drop page components. Citizen developers usually configure the last settings in the application such as assigning application admins, picking the right color scheme, and adding front-end elements where necessary.
Place in the iterative development
Citizen developers play an important role in the iterative process of application development, applying their blend of process and business-oriented vision to contribute meaningfully to the evolution of software solutions. Through continuous feedback loops, citizen developers engage in a cycle of building, testing, and refining applications, ensuring that the end product not only meets user expectations but also aligns closely with the strategic objectives of the organization.
Central to the approach of citizen developers is the concept of building applications in manageable ‘chunks’. This perspective entails viewing applications as a series of interconnected modules, each serving a specific function or addressing a particular business need. By breaking down complex functionalities into smaller, logically isolated bundles, citizen developers simplify the development process and reduce the burden associated with releasing updated features.
Conclusion
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the vital role of the citizen developer in driving digital transformation. With access to new platforms, these individuals can now address recurring issues without relying on coding skills or waiting for IT resources. They quickly turn business problems into valuable solutions through a simplified development process. While complex tasks may still require IT support, citizen developers can swiftly boost innovation and productivity gains in application development.