Property reference
Learn which property types we have to offer and what each one does.
Properties are the attributes ascribed to a model and are assigned a data type. This defines the property information - data - in terms of, for example, a number, text (string) or price type. Each new model created automatically contains the following properties:
-
Created at
-
Updated at
-
Id.
The Id property uniquely identifies every object in a model.
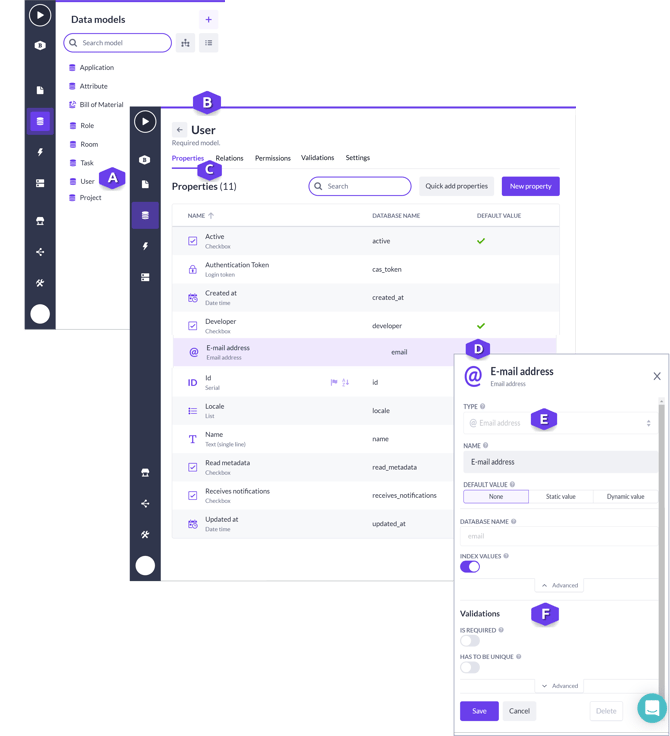
As shown in the following, the model User (A) is opened from the Models quick menu.
The details for the model are displayed (B). By default, the Properties tab (C) is opened and displays the list of properties in a model.
When you select a property, the details for the property are displayed in a separate pane. In the following example, the details for the E-mail address property (D) are shown.
As shown, properties contain details such as the Type assigned, the name and additional details such as database name. The Type assigned determines the values that can be applied to a property.
See below for more details about Type and associated fields.
If required, click on the image to expand in a new tab or window.
Property types

The property type determines the fieldset associated with a property.
When you select the New property button, the New property pane is opened. Click on the menu button in the Type field to display the list of Types available. You can assign the relevant Type to the property. Once applied, you can specify settings based on the options (field set) available for that Type.
Property options
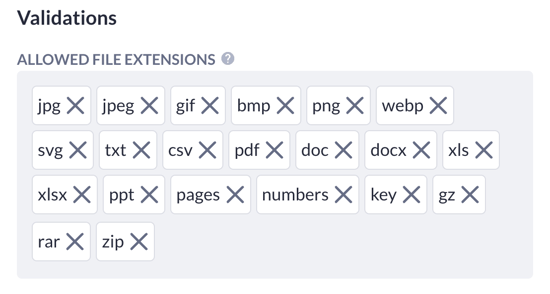
Where relevant, you can also apply specific details for a property such as validations. Validations can be used to apply rules when data is entered. For example, to require a user to enter their e-mail details when registering or to specify specific file types allowed when, for example, uploading an image file.
Validations
Is required: Determines if a value is required for a certain property.
Has to be unique: Determines if the value needs to be unique within a particular model.
Index values: With this setting enabled, the property's value will be indexed in a separate table. This table will be used when the property is included in search operations.
Database name: The database name determines how the property is called in the data API.

Name: Choose a name for the property that is used in expressions, endpoints, and Liquid syntax. It must be unique within the model.
Type: Determines what kind of data can be stored in a certain property.

You can use the information provided at the field level for guidance on the information required for fields assigned in a property.